Suicide prevention for older adults has emerged as a critical public health concern given the rising elderly suicide rates, particularly among those aged 75 and older. Despite their escalating need, many seniors struggle to find accessible mental health resources tailored to their unique challenges and experiences. Recent studies have shown a significant gap in the availability of effective suicide prevention awareness specifically aimed at this demographic, highlighting an urgent call for action. In response, healthcare professionals are advocating for enhanced geriatric mental health initiatives that leverage online suicide resources for seniors, aiming to mitigate factors like social isolation and loneliness. By focusing on this vulnerable population, we can foster a supportive environment where older adults can access crucial mental health support and potentially save lives.
As society grapples with the issue of elderly suicide rates, it is essential to examine care strategies designed for senior citizens facing severe mental health challenges. Targeted solutions are necessary to improve suicide prevention measures for the older population, considering the distinct complexities they encounter. A growing emphasis on mental well-being among older individuals highlights the need for tailored initiatives and online suicide resources that cater specifically to their concerns. By fostering awareness about the mental health needs of seniors, we can cultivate an informed and supportive community that prioritizes their emotional health. It is a collective responsibility to ensure that effective suicide prevention strategies are not only recognized but also readily available to our elderly citizens.
The Alarming Increase in Elderly Suicide Rates
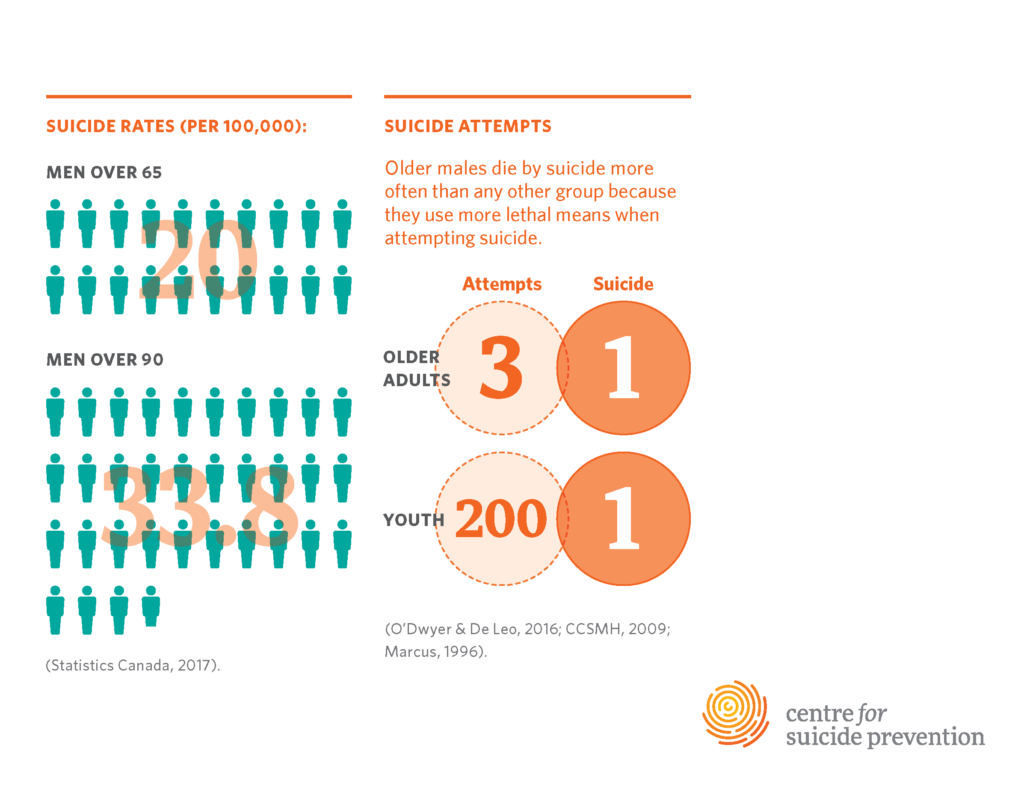
Recent statistics reveal that the elderly population, particularly those aged 75 and older, faces the highest suicide rates compared to any other age group. This troubling trend not only highlights the urgent need for mental health resources for seniors, but also emphasizes a growing crisis that often goes unnoticed. Factors such as social isolation, loneliness, and a lack of accessible support systems contribute to this alarming increase. Research indicates that while many organizations recognize the significance of this issue, the resources available specifically for older adults are woefully inadequate.
With the CDC reporting a suicide rate of 20.3 per 100,000 for adults over 75, it’s clear that immediate action is needed. The systematic oversight of the elderly in mental health campaigns raises important questions about how well current initiatives serve this vulnerable demographic. Many traditional suicide prevention strategies overlook the unique circumstances and challenges faced by older adults, making it imperative to tailor these resources for more effective outreach and support.
Tailored Suicide Prevention Awareness for Seniors
One critical aspect of enhancing suicide prevention efforts for older adults is the development of tailored campaigns that address their specific needs. The study conducted by McLean Hospital highlights that general public-facing suicide prevention campaigns are not sufficiently reaching this demographic. By focusing on the elderly population’s distinct circumstances, organizations can create specialized materials and programs that resonate better with older adults, making them feel understood and supported.
Additionally, the integration of geriatric mental health professionals in these initiatives can significantly increase effectiveness. Clinicians who specialize in elderly care can bring invaluable insights into how to appeal to this age group, thereby improving engagement in mental health resources for seniors. A collaborative approach that includes older adults in the conversation about their mental health not only increases awareness but empowers them to seek help when necessary.
Online Suicide Resources for Seniors: A Growing Need
In today’s digital age, the internet serves as a primary resource for individuals seeking health information, including mental health support. The study from McLean shows that while older adults are increasingly using the internet, the availability of tailored online suicide resources remains limited. This discrepancy highlights the need for organizations to innovate and create user-friendly platforms that can effectively meet the unique needs of older adults facing mental health challenges.
Online suicide resources for seniors must not only be easily accessible but should also incorporate content that resonates with their experiences. Initiatives aiming to educate seniors about the signs of mental distress and available support services can foster a culture of openness and help-seeking behavior. By enhancing the visibility of these resources in digital spaces, organizations can play a vital role in preventing suicide among the elderly.
The Importance of Mental Health Resources for Seniors
Mental health resources for seniors are crucial in addressing the growing concern of suicidal ideations and actions among older adults. These resources must encompass a breadth of support options, including counseling, crisis hotlines, and community programs specifically designed for seniors. The recent findings from the McLean study underline that there is a significant gap in the availability of these resources, posing a risk to an already vulnerable population.
Moreover, equipping older adults with knowledge about mental health resources can significantly reduce stigma associated with seeking help. Initiatives made by healthcare organizations to promote awareness and accessibility can help in creating a society where older adults feel comfortable reaching out for support. This is essential not only for prevention but also for ensuring that elderly individuals can live fulfilling lives, free from the grips of isolation and despair.
Integrating Geriatric Mental Health Strategies
Integrating geriatric mental health strategies into existing mental health frameworks is vital for effectively addressing the unique challenges faced by older adults. This involves not only developing specific resources but also training healthcare professionals to understand the nuances of geriatric psychology. A multifaceted approach that emphasizes empathy, tailored communication, and support can significantly improve the mental well-being of older adults.
Furthermore, collaboration between mental health professionals, community organizations, and the healthcare system is essential. Creating a network that prioritizes the mental health of seniors can lead to more successful outcomes, reducing the risk of suicide in this demographic. By prioritizing geriatric mental health strategies, society can take crucial steps toward creating a supportive environment that encourages healthier aging.
Community Engagement in Suicide Prevention
Community engagement plays a pivotal role in suicide prevention among older adults. By fostering connections within the community, barriers to seeking help can be lowered. Local programs that involve seniors in activities, workshops, and outreach initiatives not only promote mental health awareness but also combat loneliness and social isolation, which are significant risk factors for suicide.
Additionally, involving families and caregivers in suicide prevention efforts is crucial. Ensuring they are aware of the signs of mental distress and the resources available can empower them to act when required. By creating a network of support around older adults, communities can significantly contribute to reducing the suicide rates within this population.
Advocating for Increased Funding in Mental Health Research
Advocating for increased funding in mental health research focused on older adults is essential for developing effective suicide prevention strategies. Research funding can lead to innovative solutions and programs that specifically address the complexities of late-life mental health. By understanding the underlying issues faced by seniors, such as social isolation and health declines, researchers can create targeted interventions.
Moreover, organizations and advocates can work together to lobby for policies that prioritize geriatric mental health initiatives, ensuring these issues are included in broader health discussions. Increased funding can support comprehensive approaches that incorporate education, access to resources, and community engagement, ultimately saving lives and improving the quality of life for older adults.
Raising Awareness about Elderly Suicide Prevention
Raising awareness about elderly suicide prevention is crucial for developing a proactive approach to this growing concern. By increasing visibility and understanding of the issue, communities can better engage with older adults and encourage them to speak up about their mental health needs. Public campaigns focusing on the signs of depression and suicidal thoughts in older adults can help demystify these topics and promote help-seeking behavior.
Furthermore, training for healthcare providers and community members to recognize suicidal risk factors can significantly enhance intervention efforts. Empowering individuals with knowledge about elderly suicide prevention fosters a culture where mental health can be openly discussed and treated without stigma, ultimately leading to a healthier, more supportive environment for older adults.
Utilizing Telehealth for Elderly Mental Health Support
Telehealth has emerged as a valuable tool for providing mental health support to older adults, particularly in light of mobility challenges and geographic isolation. Utilizing this technology can bridge the gap in access to mental health resources for seniors, allowing them to seek help from the comfort of their homes. Telehealth services can include therapy sessions, support groups, and crisis interventions, all tailored to meet the unique needs of the elderly population.
Additionally, developing user-friendly telehealth platforms that cater to older adults’ technological comfort levels is crucial. By optimizing these services and ensuring they are easily accessible, healthcare providers can realize the potential of telehealth to reduce suicide risk among older adults while promoting ongoing mental health care.
The Role of Family in Suicide Prevention for Older Adults
Families play a critical role in the prevention of suicide among older adults. Encouraging open dialogue about mental health within families can help reduce stigma and create an environment where older relatives feel comfortable discussing their feelings. Family members who are informed about the signs of mental distress can be proactive in seeking help for their loved ones, leading to timely interventions when necessary.
Moreover, education programs targeting families can provide them with tools and strategies to support their elderly relatives, fostering a collaborative approach to mental health care. By working together, families can create a robust support network that not only prioritizes mental health resources but also actively engages in the conversation surrounding elderly suicide prevention.
Frequently Asked Questions
What mental health resources for seniors are available for suicide prevention?
Mental health resources for seniors focused on suicide prevention include helplines such as the National Suicide Prevention Lifeline, which offers support specifically for older adults. Additionally, organizations like AARP provide valuable information and guidance on mental health services tailored for seniors. Comprehensive resources can also be found through local mental health clinics that specialize in geriatric mental health.
What are the elderly suicide rates and how can they be addressed?
Elderly suicide rates, particularly among adults aged 75 and older, are alarmingly high at 20.3 per 100,000 individuals. Addressing these rates involves implementing targeted suicide prevention awareness campaigns and improving access to mental health resources for seniors. This includes enhancing online accessibility to resources specifically designed to meet the needs of older adults.
How can online suicide resources for seniors be improved?
Online suicide resources for seniors can be improved by ensuring that websites are user-friendly and easily navigable for older adults. This includes having larger text, simple language, and prominent links to suicide prevention resources. Organizations should enhance their online presence through search engine optimization strategies that feature geriatric mental health services prominently for this vulnerable demographic.
What role does social isolation play in elderly suicide rates?
Social isolation significantly contributes to the high suicide rates among older adults, as feelings of loneliness and abandonment can lead to suicidal thoughts. Effective suicide prevention for older adults must integrate strategies to combat social isolation, such as community engagement programs and support groups specifically designed for seniors.
How can families support older adults in suicide prevention efforts?
Families can support older adults by encouraging open conversations about mental health, being aware of signs of depression or suicidal thoughts, and actively engaging them in social activities. Additionally, families should familiarize themselves with mental health resources for seniors and facilitate access to these services when needed.
Why is there a need for geriatric mental health focused suicide prevention?
There is a critical need for geriatric mental health-focused suicide prevention because older adults face unique challenges that differ from younger populations, such as chronic health issues, loss of loved ones, and increased social isolation. Tailored strategies are necessary to effectively address the specific needs and circumstances of older adults in order to reduce suicide rates in this demographic.
What initiatives exist to raise suicide prevention awareness among older adults?
Initiatives to raise suicide prevention awareness among older adults include public health campaigns and educational programs targeting seniors. These initiatives often focus on increasing awareness of mental health resources for seniors and providing information on recognizing suicidal signs, thereby empowering older adults to seek help.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Older Adults Risk | Older adults aged 75 and over have the highest rates of suicide among any age group. |
| Resource Availability | National suicide prevention organizations provide limited resources specifically for older adults. |
| Study Findings | A study from McLean Hospital reveals an imbalance in targeting online suicide prevention efforts for older adults. |
| Contributing Factors | Factors such as social isolation, loneliness, and implicit biases contribute to rising suicide rates. |
| Call for Action | There is a need for tailored campaigns and increased funding for suicide prevention resources aimed at older adults. |
Summary
Suicide prevention for older adults is a critical issue that demands immediate attention and actionable solutions. The alarming rise in suicide rates among individuals aged 75 and older highlights the necessity for tailored prevention resources to meet their unique healthcare needs. As this vulnerable demographic increasingly turns to online resources for help, it is vital that national organizations address the gaps in available information and support. By implementing targeted campaigns and enhancing accessibility, we can work towards reducing the stigma around mental health in older populations and providing the necessary support to combat this pressing concern.