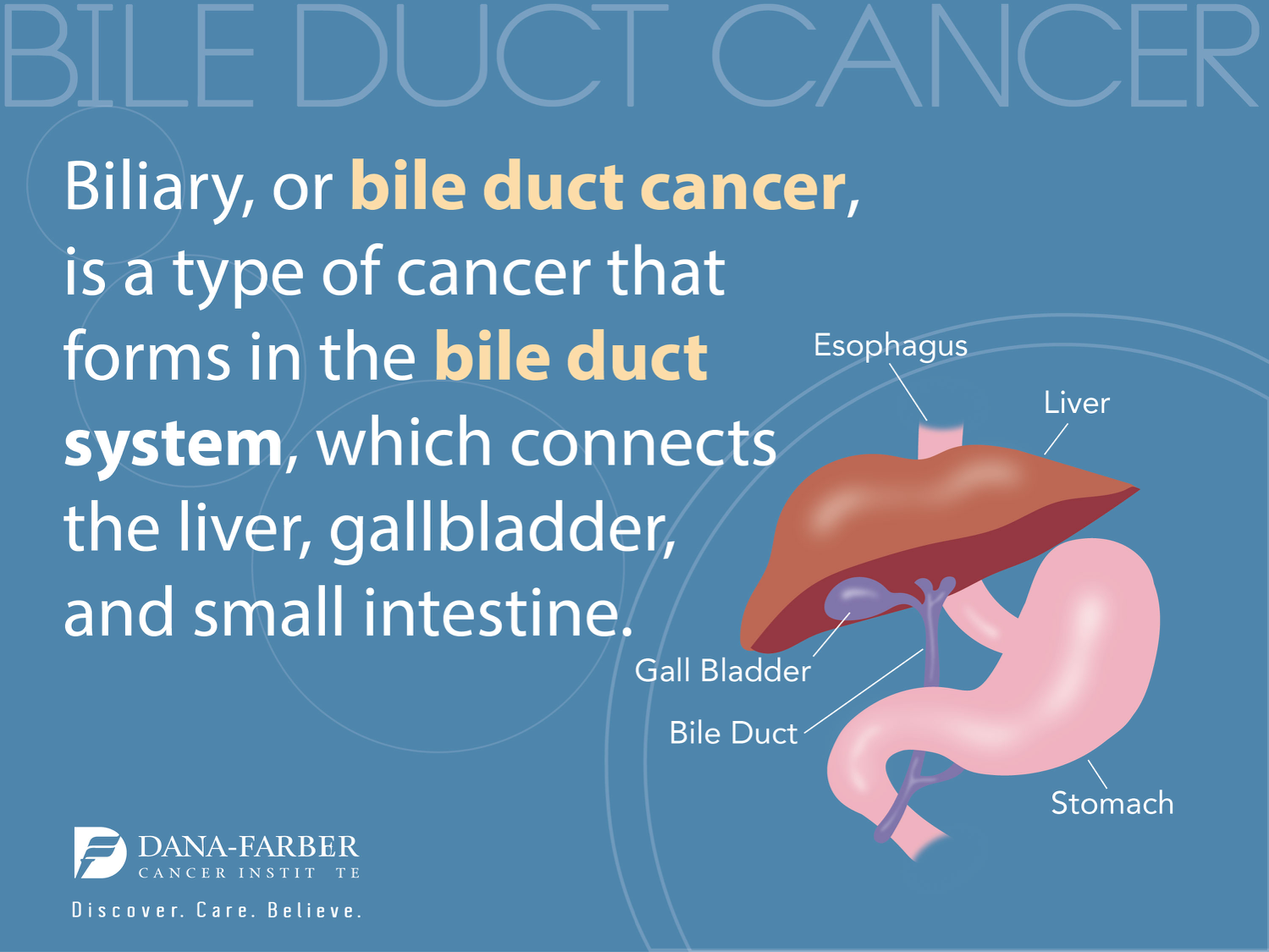
Bile imbalance liver cancer is emerging as a significant area of concern in the realm of hepatology, as new research highlights the crucial link between bile acids and the development of liver diseases, particularly Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC). Bile acids, primarily produced by the liver, play a vital role in the digestion of fats and maintaining metabolic equilibrium, but an imbalance can have dire consequences. The recent discovery of a key molecular switch that regulates bile acid production could pave the way for innovative liver cancer treatments, offering hope to those affected by this aggressive cancer type. Notably, this research sheds light on the interplay between the FXR receptor and the YAP signaling pathway, revealing how disruptions in bile metabolism can lead to liver injury and cancer progression. As we continue to unravel the complexities of bile acids function, it becomes ever clearer that addressing bile imbalance liver cancer may open new avenues for effective therapeutic interventions.
The relationship between bile acid dysregulation and cancer of the liver, particularly hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), is garnering increasing attention in medical research. This condition, often triggered by disruptions in the balance of bile acids, highlights the liver’s intricate role in metabolic processes and fat digestion. The identification of critical molecular pathways, including the FXR nuclear receptor and YAP signaling mechanisms, can lead to novel strategies for liver cancer treatment. Understanding the hormonal-like functions of bile acids allows researchers to explore therapeutic interventions aimed at restoring balance and preventing the onset of liver malignancies. As the investigation into bile acids continues, it becomes clear that enhancing bile acid homeostasis may be key in combating liver cancer effectively.
Understanding Bile Imbalance and Its Role in Liver Cancer
Bile imbalance, particularly linked to liver cancer, specifically Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC), has garnered attention due to its critical impact on liver health. Bile acids, produced by the liver, are not only essential for fat digestion but also play a regulatory role in various metabolic processes. When the production and regulation of bile acids are disrupted, it can lead to detrimental outcomes such as liver inflammation, damage, and progression to cancer. A recent study has thrown light on this relationship, suggesting that disturbances in bile acid homeostasis could be a pivotal factor triggering the onset of HCC.
The study highlights a key molecular switch that controls bile acid metabolism, showcasing the intricate interconnections between bile acids and liver cancer. By focusing on the YAP signaling pathway, researchers have uncovered how YAP can promote tumor formation by interfering with the function of a crucial bile acid receptor called FXR. This interaction showcases the importance of maintaining a delicate balance in bile acid levels, as an overload can lead to significant liver damage and cancer progression.
The Molecular Mechanisms Behind Bile Acid Regulation
At the heart of bile acid regulation lies the FXR receptor, which is essential for maintaining bile acid homeostasis in the liver. When functioning optimally, FXR helps regulate the production and excretion of bile acids, thus preventing their accumulation. However, the activation of the YAP signaling pathway can inhibit FXR’s activity, leading to excess bile acids in the liver. This pathological condition fosters an environment conducive to liver inflammation and fibrosis, which are recognized precursors to liver cancer. Understanding these molecular mechanisms is vital for developing targeted therapeutic strategies for liver cancer treatment.
Moreover, the recent findings underscore an exciting avenue for potential liver cancer treatments that could stimulate FXR function. By enhancing the activity of this nuclear receptor, researchers hope to restore the balance of bile acids, mitigate liver damage, and prevent the progression of cancer. Techniques such as inhibiting HDAC1, which enables YAP’s repressive functions, or increasing the expression of bile acid export proteins like BSEP may provide new therapeutic options that target these pathways effectively.
Innovative Treatment Approaches for Liver Cancer
Considering the insights garnered from the research on bile imbalance and liver cancer, there is potential for innovative treatment approaches that leverage our understanding of the FXR receptor and YAP signaling pathway. Enhanced pharmacological strategies that activate FXR could significantly alter the course of disease by promoting healthy bile acid metabolism and reducing liver toxicity. This approach not only addresses the symptoms of liver damage but also targets the underlying molecular disruptions that contribute to the development of Hepatocellular Carcinoma.
In conjunction with pharmacological interventions, lifestyle modifications aimed at improving liver health can play a crucial role in cancer prevention. For instance, maintaining a balanced diet that supports liver function, regular exercise, and avoiding substances that can exacerbate bile imbalance are vital components of a holistic approach to liver cancer prevention. Enhanced public awareness and education about bile acids’ functions and their implications for liver health are essential for fostering preventive measures against liver cancer.
YAP Signaling Pathway: A Target for Liver Cancer Therapy
The signaling pathway mediated by YAP has emerged as a critical focus for liver cancer research. Given its role in regulating bile acid metabolism and promoting tumor growth, targeting YAP could provide a novel therapeutic approach for treating Hepatocellular Carcinoma. By developing inhibitors that block YAP’s repressive activities on FXR, researchers could restore bile acid homeostasis and reduce the risk of cancer development. This strategy could also complement existing liver cancer treatments, enhancing their effectiveness.
Moreover, the identification of specific biomarkers within the YAP signaling pathway could enable personalized medicine approaches, allowing for more tailored liver cancer treatments based on an individual’s molecular profile. Such advancements will not only improve patient outcomes but also contribute to a better understanding of the complex interplay between bile acids, liver function, and cancer biology.
The Critical Role of FXR in Liver Health
Farnesoid X receptor (FXR) plays a pivotal role in the regulation of bile acids and their metabolism. This nuclear receptor is activated by bile acids and, in turn, regulates their synthesis, transport, and excretion, maintaining a delicate balance crucial for liver health. When FXR is functioning properly, it can prevent bile acid accumulation, thus reducing the risk of liver inflammation and subsequent development of conditions such as Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Researchers are now focusing on strategies to bolster FXR activity to mitigate liver cancer risk.
Additionally, ongoing studies are exploring how FXR interacts with various metabolic pathways in the liver. These interactions may provide insights into broader metabolic control mechanisms that influence liver diseases. By understanding the comprehensive role of FXR, researchers hope to develop novel therapeutic avenues targeting liver cancer and other metabolic disorders associated with bile acid dysregulation.
Bile Acids: Beyond Digestion to Disease
Bile acids, traditionally viewed as mere facilitators of fat digestion, are now recognized for their complex roles in metabolic regulation and liver disease pathology. They function not only as digestive agents but also as signaling molecules that influence various biological processes. The dual function of bile acids underscores their importance in maintaining liver health, as imbalances can lead to significant health issues, including liver cancer. Research is now delving into how bile acids communicate with other metabolic pathways and how disruptions in this communication can lead to disease.
These insights are prompting a reevaluation of how we approach liver health. By understanding the systemic effects of bile acids and their role in conditions such as Hepatocellular Carcinoma, healthcare providers can develop more effective preventative and therapeutic strategies. This shift in perspective is crucial as we work towards therapies that improve liver function and counteract the adverse effects of bile acid imbalances.
Clinical Implications of Bile Acid Research
The findings regarding bile imbalance and liver cancer have significant clinical implications, particularly in the realm of treatment development. As researchers identify the critical roles of FXR and YAP signaling pathways in bile acid metabolism, there is an opportunity to translate these discoveries into therapeutic interventions. Clinical trials exploring FXR agonists, which may help restore bile acid homeostasis, could lead to groundbreaking liver cancer treatments that improve survival rates for patients.
In addition, these insights encourage the medical community to consider bile acid levels as potential biomarkers for early detection and monitoring of liver health. Monitoring bile acid homeostasis may provide valuable prognostic information regarding liver disease progression. As research progresses, the integration of this knowledge into clinical practice could enhance patient care and outcomes in liver cancer.
Future Directions for Bile Acid Research
As we look to the future of bile acid research, there are numerous avenues for exploration that could yield valuable insights into liver health and cancer prevention. Continued investigations into the mechanisms governing bile acid metabolism, particularly the interactions between FXR and YAP, will be essential in developing targeted therapies. Moreover, understanding how lifestyle factors and dietary choices impact bile acid composition could offer additional strategies for liver cancer prevention.
Furthermore, advancements in genomic and molecular techniques will facilitate deeper investigations into the genetic and molecular bases of bile acid dysregulation. By uncovering these underlying mechanisms, researchers can identify new therapeutic targets and biomarkers, ultimately leading to the development of more effective strategies to combat liver cancer and promote liver health.
Educational Initiatives on Liver Health and Bile Imbalances
Public health initiatives aimed at educating individuals about liver health and the critical role of bile acids could significantly alter the landscape of liver disease prevention. Raising awareness around the symptoms of liver dysfunction, risk factors for Hepatocellular Carcinoma, and the importance of maintaining a balanced diet is crucial in empowering individuals to take proactive measures regarding their health. Educational programs should focus on the relationship between bile acids and liver cancer, emphasizing the need for regular medical check-ups and monitoring liver health.
Additionally, healthcare providers should be equipped with the knowledge to discuss bile balance and liver health with patients effectively. By integrating this information into routine consultations, physicians can inspire their patients to adopt healthier lifestyles that support liver function. As more discoveries unfold in the realm of bile acid research, it becomes increasingly important to disseminate this information for the benefit of public health.
Frequently Asked Questions
How is bile imbalance related to liver cancer treatments?
Bile imbalance plays a critical role in liver cancer treatments, particularly for Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC). Disruptions in bile acid metabolism can lead to liver injury and cancer progression. New therapies aim to address this imbalance by targeting the FXR receptor, which regulates bile acids. Enhancing FXR function can help restore bile homeostasis and potentially inhibit cancer growth.
What is the connection between bile acids function and Hepatocellular Carcinoma?
Bile acids contribute significantly to liver health and function. In the context of Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC), an imbalance in bile acids can trigger inflammation and fibrosis. The FXR receptor, which is crucial for maintaining bile acid levels, is often inhibited by YAP signaling in liver cancer. This disruption exacerbates liver damage, making understanding bile acids function essential for developing effective treatments.
What role does the FXR receptor play in bile imbalance linked to liver cancer?
The FXR receptor is vital for bile acid homeostasis and helps maintain liver health. In cases of bile imbalance associated with liver cancer, particularly Hepatocellular Carcinoma, FXR is often inhibited by YAP signaling. This leads to overproduction of bile acids, contributing to liver inflammation and cancer progression. Targeting FXR can thus offer therapeutic strategies for restoring balance and combating liver cancer.
How does the YAP signaling pathway affect bile acid metabolism and liver cancer?
The YAP signaling pathway plays a dual role in liver physiology and cancer. In the case of bile acid metabolism, YAP activation has been found to repress the FXR receptor, leading to bile acid accumulation and subsequent liver damage. This process is significant in the context of Hepatocellular Carcinoma, as it promotes cancer development. Understanding this pathway can inform new liver cancer treatments aimed at reversing the effects of YAP on bile metabolism.
Can improving bile acid excretion impact liver cancer progression?
Yes, enhancing bile acid excretion can significantly impact liver cancer progression. When the liver’s ability to remove excess bile acids is compromised, it can lead to inflammation and fibrosis, which are precursors to Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC). Researchers suggest that therapies aimed at promoting bile acid exportation, such as increasing the expression of BSEP proteins, may help prevent the damage associated with bile imbalance, thereby reducing cancer risks.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Bile Imbalance and Liver Cancer | Imbalance in bile acids can trigger liver diseases, including Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC). |
| Research Findings | A study identified a key molecular switch that regulates bile acid production affecting liver health. |
| Role of YAP | YAP, a regulator of cell growth, inhibits FXR, leading to bile acid overproduction and liver inflammation. |
| Potential Treatments | Blocking YAP’s activity or enhancing FXR function may reduce liver damage and cancer risk. |
| Broader Implications | Understanding YAP’s role could lead to novel pharmacological solutions targeting bile metabolism. |
Summary
Bile imbalance related to liver cancer is a critical health concern that has gained attention in recent studies. Recent findings have linked the regulation of bile acids to the development of Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC), the most prevalent form of liver cancer. By uncovering the molecular mechanisms behind bile production and its effect on liver health, researchers have identified targets for potential treatments. These insights reveal the importance of maintaining bile acid homeostasis to mitigate liver injury and prevent cancer progression.