Is sugar addictive? This age-old question sparks intense debate among nutritionists and health experts alike. While cravings for sugar can mimic those of more notorious substances like alcohol and nicotine, current clinical definitions do not classify sugar as an addictive substance. However, the effects of sugar on our bodies and minds are undeniable, often leading to an habitual pattern of consumption. Understanding sugar addiction’s nuances is vital as it directly impacts our health, urging us to consider not only sugar consumption recommendations but also its broader implications on our well-being.
The concept of sugar as an addictive substance often raises eyebrows due to its omnipresence in modern diets. Some refer to it as a common crave-inducing ingredient that, while not officially deemed addictive, can lead to significant health concerns. The term ‘sugar cravings’ encompasses the strong desire many people feel for sweet foods, highlighting its powerful allure. Moreover, the physiological reactions to high sugar intake can be likened to those triggered by other substances, blurring the lines between necessity and indulgence. As we navigate the complexities of our cravings and overall health, it is essential to engage with sugar consumption thoughtfully, balancing enjoyment with mindful eating.
Understanding Sugar Addiction
The question of whether sugar is addictive has sparked extensive debate among nutritionists and health professionals. While substances such as alcohol, nicotine, and opiates are classified as addictive based on clinical criteria, sugar presents a more nuanced case. Research indicates that sugar can lead to cravings and compulsive eating behaviors, similar to those seen with other addictive substances. Individuals may experience withdrawal-like symptoms such as headaches and anxiety when they stop consuming high amounts of sugar, raising the conversation about whether sugar could be viewed through the same lens as drug addictions.
However, distinguishing sugar from addictive substances like nicotine is crucial due to the inherent nutritional value sugar provides. Sugar is naturally present in many foods, including fruits, vegetables, and dairy products. This variability in context suggests that while sugar may promote cravings and habitual consumption, it is not a substance that can be entirely eliminated from our diets without affecting our nutritional intake. Instead of an all-or-nothing approach, moderation plays a vital role in managing sugar consumption and maintaining overall health.
Effects of Sugar on Health
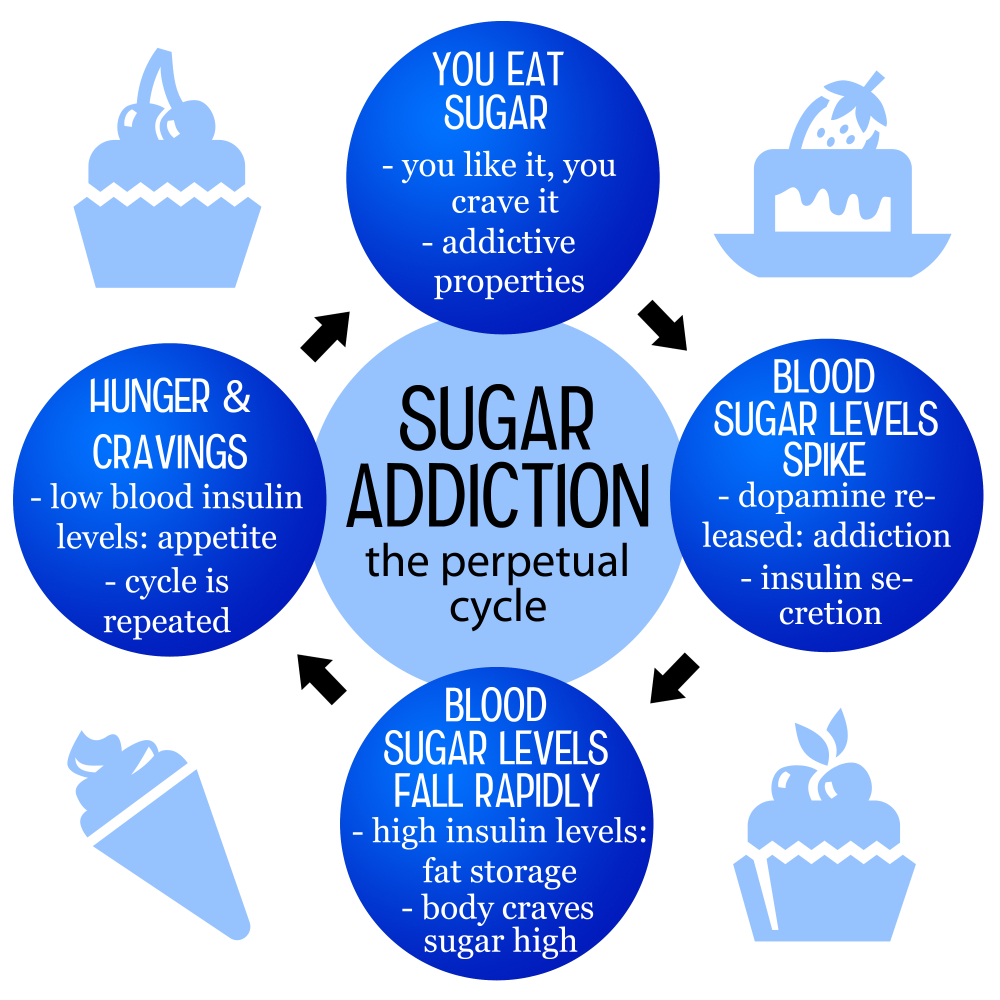
The effects of sugar on health are profound and multifaceted. High consumption of added sugars is linked to various health issues such as obesity, diabetes, and heart disease. The typical American diet, which includes large amounts of sugary beverages and processed foods, often exceeds the recommended intake of added sugar significantly. The American Heart Association advises that men should limit their intake to 9 teaspoons per day and women to 6 teaspoons. Exceeding these recommendations can lead not just to weight gain but also to increased cravings for sugar, creating a vicious cycle that can harm one’s health.
Moreover, the highly palatable nature of sugary foods drives many people to consume them in excess. This excessive consumption can lead to rapid spikes in blood sugar levels, resulting in hormonal responses that further trap individuals in cycles of cravings for sugar. Understanding the health implications of sugar consumption is more critical than ever, as being aware of what is in our food — checking labels and making informed choices — can empower individuals to reduce their sugar intake and improve their long-term health results.
How Cravings for Sugar Develop
Cravings for sugar often develop from our body’s responses to the sweet taste and the rapid energy boosts it provides. These cravings can be triggered by a variety of factors, including emotional states, environmental cues, and even food marketing. When we consume sugar, our bodies release dopamine, the feel-good hormone, reinforcing the behavior and leading to habitual consumption. Over time, the brain begins to associate the sweet taste with reward, making it harder to resist sweet treats even when we are not hungry.
Additionally, cravings can also be exacerbated when individuals try to drastically cut sugar from their diets. This approach can lead to withdrawal symptoms that spark a desire to return to sugary foods, further complicating one’s relationship with sugar. To effectively manage cravings, it’s essential to adopt a balanced approach that includes sugar moderation rather than complete deprivation. Gradually reducing sugar intake while replacing highly processed foods with healthier options can help in overcoming these cravings while still enjoying a flavorful, satisfying diet.
Sugar Consumption Recommendations
To navigate the complexities of sugar consumption, adhering to recommendations provided by health organizations is crucial. The American Heart Association and other health bodies offer guidelines for added sugar intake aimed at promoting better health outcomes. Staying within the suggested limits not only reduces the risk of health problems associated with high sugar consumption but also allows individuals to savor the sweetness of naturally occurring sugars found in fruits and dairy without excess.
Practical tips for reducing added sugars include being mindful of hidden sugars in processed foods, reading nutrition labels meticulously, and opting for whole-food alternatives. Instead of sugary snacks, incorporating fruits, nuts, and whole grains can satisfy sweet cravings while delivering essential nutrients. Establishing these healthy habits creates a more sustainable lifestyle, allowing people to enjoy their favorite foods without compromising their health.
Balancing Sugar in a Healthy Lifestyle
Striking a balance when it comes to sugar consumption is critical for maintaining overall health. While sugar does indeed have addictive qualities, particularly in its most processed forms, it also serves a purpose in our diets when consumed appropriately. Incorporating moderate amounts of sugar within a diet rich in whole foods can amplify flavors and enhance meals. Understanding how to balance sugar intake while prioritizing nutrient-dense foods is essential for achieving a healthy lifestyle.
Moreover, fostering a positive relationship with food includes allowing oneself to enjoy sweet treats occasionally. This mindset helps avoid the guilt associated with eating sugar, which can lead to unhealthy behaviors and cravings. Emphasizing moderation, mindfulness, and variety in our diets allows us to embrace sweetness without falling into the traps of addiction or excessive consumption. By making informed choices, managing portions, and enjoying the occasional indulgence, individuals can enjoy sugar within a balanced, health-promoting framework.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is sugar addiction and is sugar addictive?
Sugar addiction refers to the compulsive consumption of sugary foods and the cravings associated with them. While sugar has been shown to increase cravings and certain compulsive behaviors, it is not classified as an addictive substance like alcohol or nicotine. However, its effects on the brain can create a desire for more sugar, leading to habitual consumption.
What are the effects of sugar on health and is sugar addictive?
The effects of sugar on health can include weight gain, increased risk of diabetes, and heart disease, alongside cravings for more sugar. Although it may lead to withdrawal-like symptoms when reduced, sugar does not meet the strict clinical criteria for addiction like other substances do. Moderation is key, as excessive sugar consumption has significant health consequences.
How do cravings for sugar relate to the concept of sugar addiction?
Cravings for sugar can often mimic the patterns of addiction, where individuals may feel unable to control their intake. This is due to sugar’s palatability and its prevalence in processed foods, which heightens cravings. While these behaviors suggest some addictive qualities, sugar is not classified as an addictive substance according to formal criteria.
Is there a relationship between sugar consumption recommendations and sugar addiction?
Yes, sugar consumption recommendations set limits on the amount of added sugar one should consume to maintain health and minimize cravings. The American Heart Association recommends no more than 6 teaspoons for women and 9 teaspoons for men. Adhering to these guidelines can help manage cravings for sugar and reduce the risks associated with high sugar intake.
What should one know about sugar and health concerning sugar addiction?
Understanding sugar and health is essential because while sugar is a natural part of various foods, excessive added sugar can lead to health issues. Signs of sugar addiction might include intense cravings, but unlike substances like alcohol and nicotine, sugar is necessary for survival in moderation. Educating oneself about sugar content in foods can aid in managing consumption.
Can reducing sugar intake help with sugar addiction symptoms?
Yes, gradually reducing sugar intake can alleviate withdrawal-like symptoms and cravings for sugar without triggering a strong counterproductive reaction often seen with abrupt cuts. This method allows individuals to adjust their diets and manage cravings effectively, emphasizing moderation rather than elimination.
Are there alternatives to sugar that can help manage cravings for sugar?
There are many alternatives to sugar, such as natural sweeteners like stevia or monk fruit. These can help satisfy sweet cravings without the health risks associated with added sugars. However, it’s important to use them in moderation and not depend solely on them to avoid cravings for sugar.
Is it possible to have a healthy relationship with sugar despite its addictive qualities?
Absolutely. Having a healthy relationship with sugar involves understanding its role in your diet, moderating consumption of added sugars, and choosing whole foods with natural sugars, like fruits. This balanced approach helps avoid cravings for sugar while still enjoying a naturally sweet taste in foods.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Sugar Addiction Debate | Sugar increases cravings and compulsive eating but is not classified as addictive like alcohol or drugs. |
| Food System Influence | Ultra-processed foods loaded with sugar lead to heightened cravings due to their palatability. |
| Withdrawal Symptoms | Stopping sugar suddenly can lead to headaches, anxiety, but symptoms are less severe than drug withdrawal. |
| Need for Sugar | Sugar is a natural part of many healthy foods; moderation is key rather than complete elimination. |
| Health Recommendations | Daily intake should be limited to 9 teaspoons for men and 6 for women according to the American Heart Association. |
| Gradual Reduction | Reducing added sugar intake gradually is advised over quitting cold turkey to avoid backlash. |
| Sugar’s Role in Diet | Sugar can enhance flavor and pleasure when consumed in appropriate amounts and is necessary in diets. |
Summary
Is sugar addictive? While there is ongoing debate about sugar’s addictive qualities, it is essential to understand that it does not meet the clinical criteria for addiction as substances like alcohol or nicotine do. This differentiation is crucial because while sugar can lead to cravings and compulsive eating, it is a natural part of many nutritious foods and essential for enjoyment in our diets. Moderation is key—keeping added sugars to recommended levels can help mitigate negative health effects and maintain a balanced approach to eating.